Ensuring Security: Best Practices for MongoDB Protection
Written on
Introduction to MongoDB Security
MongoDB stands out as a widely-used open-source NoSQL database known for its flexible, schema-less data storage format that utilizes BSON (binary JSON) documents. Its dynamic structure allows for a varying number of fields, making it a popular choice among developers. However, given that MongoDB often holds sensitive data, safeguarding its security and ensuring constant accessibility is paramount for organizations. By implementing robust security measures, the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access can be significantly diminished. This discussion will delve into the various strategies for securing MongoDB effectively.
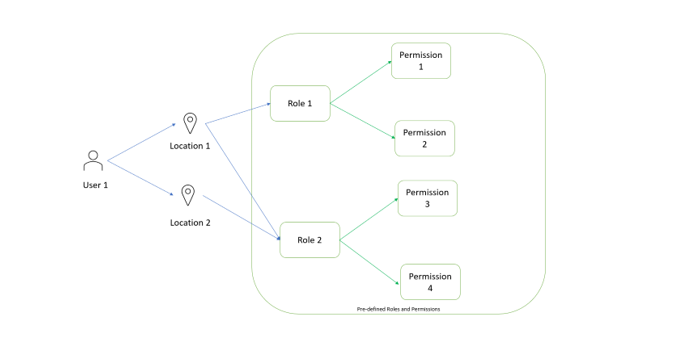
Role-Based Access Control in MongoDB
To prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other critical security issues, proper configuration of MongoDB is essential.
A user can be assigned multiple roles, each with distinct permissions. If a user holds several roles, they gain access to all associated privileges. MongoDB comes equipped with predefined roles, and administrators have the flexibility to create custom roles as needed. Examples of default roles include read/write, dbAdmin, userAdmin, and clusterAdmin. It is crucial for administrators to assign only the minimum required permissions to users to mitigate the risk of accidental or deliberate misuse.
For instance, consider the following user creation command:
db.createUser({
user: "NormalUser",
pwd: "NormalPassword",
roles: ["clusterAdmin"]
})
In this example, the "NormalUser" possesses rights solely for the clusterAdmin role, ensuring that access is limited according to the user's needs.
Encryption Practices in MongoDB
Data encryption is vital for safeguarding information both at rest and during transit, thereby enhancing overall database security. To secure data transmitted between applications and the MongoDB server, transport layer security protocols such as TLS and SSL can be utilized. The following configuration settings in the mongod.conf file enable this feature:
net:
port: 11111
bindIp: 127.0.0.1/localip
ssl:
mode: requireSSL
PEMKeyFile: /path/to/mongodb.pem
The PEMKeyFile indicates the location of the SSL certificate and private key, while the requireSSL setting enforces SSL usage.
Moreover, encrypting the entire MongoDB data directory with file system-level security ensures comprehensive protection. Regularly updating encryption keys and reviewing configuration settings is also advisable to maintain data integrity and privacy.
Network Security Best Practices for MongoDB
Securing a MongoDB server from unauthorized access or data interception starts with fundamental network security measures. Configuring MongoDB to accept connections only from specific IP addresses is a critical first step. This can be achieved by modifying the mongod.conf file:
net:
bindIp: 127.0.0.1
While this example uses a local IP address, the binding IP can be adjusted according to the organization's needs. Additionally, implementing virtual firewalls and disabling unnecessary HTTP interfaces can further minimize exposure to potential threats.
To restrict network access to the MongoDB server, administrators can use firewall rules:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 27017 -s trusted_ip_address -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 27017 -j DROP
On Linux, these iptables commands help ensure that only authorized users can access the MongoDB server by enabling authentication features in the mongod.conf file:
security:
authorization: enabled
Backup Strategies for MongoDB
Establishing a solid backup strategy is crucial for data availability, security, and recovery from various threats. MongoDB provides several backup utilities, such as mongodump for creating logical copies and mongorestore for restoring data stored in BSON format.
To maximize the effectiveness of backups, businesses should adopt best practices including frequent backups, retention policies, automated backups using cron jobs, and encrypted backups. By implementing these strategies, organizations can ensure the continuous accessibility and accuracy of their data, tailored to specific criteria such as volume, recovery targets, and criticality.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of MongoDB and its security is vital. While numerous strategies could enhance security, this discussion has focused on widely adopted practices that address the most pressing risks. Organizations must incorporate these best practices to shield themselves from potential threats.
Monitoring and reviewing audit logs regularly is essential for gaining insights into database security threats and identifying necessary mitigation measures. If certain permissions are not required, consider disabling them in the configuration file to reduce potential vulnerabilities.
Explore best practices for securing MongoDB in this informative video, which covers essential techniques to protect your database from threats.
In this video, discover ten vital tips for securing MongoDB, especially in light of recent hacking incidents and ransomware attacks.