The Future of Multimaterial Inkjet Printing: A Colorful Evolution
Written on
Chapter 1: The Transformation of Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing has transcended its traditional role in document and photo reproduction, evolving into a revolutionary instrument in material science. Researchers are now able to manipulate tiny droplets with remarkable accuracy, giving rise to materials that can alter their properties or colors in reaction to mechanical stress. This advancement marks the dawn of an era filled with intelligent and functional materials.
This paragraph will result in an indented block of text, typically used for quoting other text.
Section 1.1: The Quest for Ideal Inks
The pursuit of the optimal ink is where it all starts. Scientists carefully mix polyurethane polymers of different hardness levels with a unique additive that fluoresces under mechanical stress. This mixture undergoes extensive testing to ensure it flows effortlessly through the printer nozzles, allowing for the creation of intricate patterns.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Precision of Printing
Equipped with cutting-edge inkjet technology, researchers perform a meticulous layering process. They alternate between soft and hard polyurethanes with precision, crafting materials that can detect stress and respond visually. This intricate process requires not only technological expertise but also a creative vision for the materials of the future.
To gain a deeper understanding of the advancements in material science described here, let’s examine a chart illustrating how various layers in multimaterial inkjet printing react to stress.
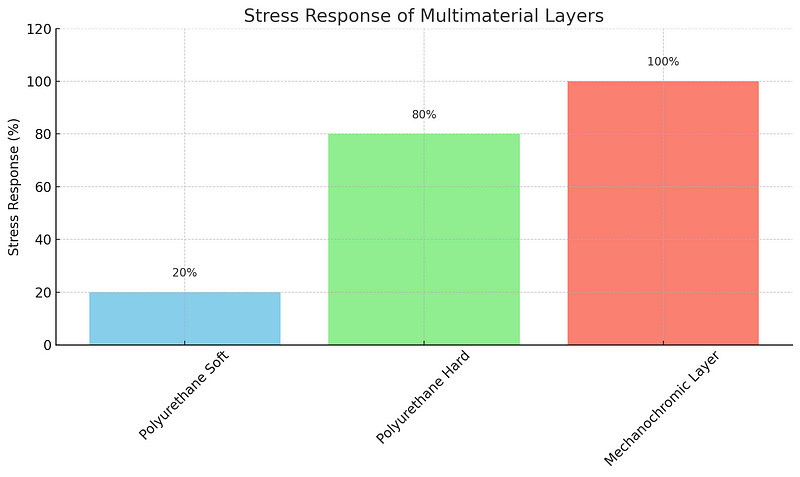
This chart showcases the diverse stress response capabilities of the soft and hard polyurethane layers, along with the mechanochromic layer, emphasizing their innovative potential in mechanical stress detection.
Section 1.2: A Colorful Reaction
When stress is applied, these materials respond vibrantly, shifting colors like chameleons based on the forces exerted on them. This stunning transformation is not just aesthetically pleasing; it has significant implications for stress detection, leading to safer structures and advanced monitoring systems.
Chapter 2: Applications Beyond the Laboratory
The first video, 4D Printing at Home - Self Assembling Magic, explores the fascinating world of 4D printing and self-assembling materials. Discover how this technology is pushing the boundaries of what we thought was possible in material creation.
The potential applications of this research extend far and wide. Envision buildings that indicate structural fatigue through color changes or bridges that visually signal wear and tear. Such technology could transform safety protocols in construction and transportation, making our world more interactive and responsive.
The second video, Making Multi-Material 3D Printed Control Panels, delves into the innovative methods behind multi-material 3D printing. Learn how these techniques are paving the way for advanced control panels and other applications.
Section 2.1: Safety Innovations
Consider a bridge that alerts engineers to stress by changing color—a plausible reality with mechanochromic materials. This technology has the potential to enhance safety in our infrastructure.
Section 2.2: The Unseen Ink
The inks utilized in this technology remain invisible until activated by pressure, revealing vibrant colors. This characteristic could transform security printing, allowing for the creation of documents that are nearly impossible to replicate.
Section 2.3: Lightweight Functionality
Despite their sophisticated functions, these advanced materials add minimal weight or bulk, integrating effortlessly into existing structures. This ensures that enhanced functionality does not compromise aesthetics or design.
Section 2.4: Wearable Technology Advancements
Wearable technology stands to benefit significantly from these materials. Clothing could monitor athletes’ stress and strain in real-time, offering instant feedback on performance and injury risks. This could mark the beginning of a new era in sports science.
Section 2.5: Environmental Monitoring
These materials could act as environmental monitors, changing color in response to pollutants or temperature fluctuations, providing an immediate and visually impactful way to assess the health of our planet.
A Hopeful Outlook
As we approach this groundbreaking era in material science, the possibilities are both vast and inspiring. These advancements promise a future where materials actively contribute to our safety, health, and environmental preservation. Although the transition from research to practical application may be challenging, the potential benefits could significantly alter our interaction with the material world. This isn’t merely the future of printing; it’s the dawn of a safer, more responsive, and visually captivating world.
About Disruptive Concepts
Welcome to @Disruptive Concepts — your window into the future of technology. Subscribe for insightful new videos every Saturday!
Watch us on YouTube